CS scrubbers
Scrubbers are devices of various designs for washing contaminated gases with liquids in order to remove one or more components from them. Centrifugal scrubbers of the CS class are dust collection units designed to clean the air from dust contamination formed during the transportation and processing of coke, quartz sand, coal, abrasives, limestone, various types of ores, etc.
In practice, these are centrifugal CS scrubbers (CS scrubber) for wet gas cleaning of gases and air: CS scrubbers are recommended for use in systems for cleaning air from dust during the processing and transportation of coke, quartz sand, abrasive materials and various ores. Such solutions work well in exhaust ventilation systems for cleaning industrial air with high dust concentration, ensuring stable efficiency and reliability of the process.
Marking of CS class scrubber
«CS - 7», where:
- «CS» - centrifugal scrubber;
- «7» - number corresponding to the inner diameter of the scrubber 700 mm.
The CS class line varies from 1000 to 10000 m³/h in terms of productivity, so the selection of the CS model is carried out according to the calculated parameters of air and gases, taking into account service and logistics (delivery in Ukraine on request).
Design advantages
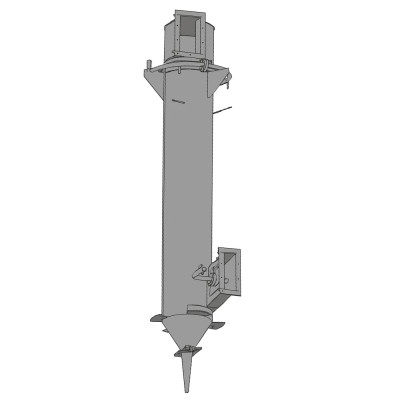
The CS class centrifugal scrubber is a hollow vertically installed cylinder. The inlet pipe for the contaminated gas is located in the lower part of the cylinder. In the upper zone around the circumference of the cylinder there are nozzles through which the liquid enters the inner surface of the cylinder to create a thin water film. Productivity in CS class scrubber models varies from 1000 to 10000 m3/h, the cylinder diameter is 300 ÷ 800 millimeters, height - 2355 ÷ 5715 millimeters, weight - 80 ÷ 407 kilograms, hydraulic resistance - 400 ÷ 850 Pa. The recommended speed of entry of the contaminated flow into these scrubbers is 15-23 m/s.
To ensure stable operation of the scrubber, the water pressure in front of the nozzles is maintained through an intermediate water tank; the nozzles evenly moisten the walls. The process parameters depend on the flow rate of contaminated air and the diameter of the cylindrical section, so the efficiency of cleaning dusty air reaches 86-90% if the recommended modes are observed (400 ÷ 850 Pa and 15-23 m/s).
For optimal scrubber operation, the water pressure in front of the nozzles must be constant and equal to 0.2 at, which is ensured by installing an intermediate water tank (ball valve). Depending on the density, dispersion of contaminants, flow rate of contaminated air and the diameter of the cylindrical section of the scrubber, the efficiency of cleaning dusty air reaches 86% - 90%. It becomes higher with increasing dust density, flow rate, and decreasing diameter of the cylindrical section. The level of purification for particles larger than 30 microns is 90%, for particles smaller than five microns it is reduced to 80%, for particles smaller than five microns it is 40%.
Operating principle
A centrifugal scrubber of the CS class is a cylinder housing, into the lower zone of which polluted air enters through the inlet pipe. In the upper zone of the housing, nozzles are installed for supplying water, which creates the thinnest water film that flows down the walls of the housing. The flow of polluted air in the scrubber cavity makes helical movements, rising to the upper zone. Due to the appearance of centrifugal force, dust particles are pressed against the walls of the unit. The displaced wet dust under the action of gravity together with water rolls down to the lower zone of the structure, forming pulp. It is removed from the unit using a drain pipe, which is closed at the right moment by a special valve. The cooled, humidified, purified air medium leaves the scrubber structure without hindrance.
Therefore, the flow of contaminated air medium flows around the wetted walls, where, due to the appearance of centrifugal force, the particles are pressed against the housing, and then - under the influence of gravity, together with water, they flow into the lower zone. Such a hollow vertically mounted cylinder with a conveniently located inlet pipe inspires easy service and reliable air cleaning from dust.
Advantages
- high dust collection efficiency;
- the possibility of simultaneously cleaning the gas flow from suspended solid particles (dust collection), cooling the gas media being cleaned (heat exchange);
- relatively low price.
The advantage of centrifugal scrubbers of the CS class is also in the flexibility of application: the scrubber can not only clean, but also cool gases in chemical and technological processes of various kinds, maintaining high efficiency when changing modes.
Field of application
Centrifugal scrubbers of the CS class are widely used in the capture coking products, cleaning industrial gas mixtures from dust, for cooling and humidifying gas environments in chemical and technological processes of various kinds. Centrifugal scrubbers of class CS are in demand in exhaust ventilation systems for cleaning air contaminated with dust generated during transportation, as well as processing of limestone, quartz sand, abrasive materials, coal, various ores, coke, etc.
Class CS scrubbers are used:
- first stage of cleaning:
- exhaust ventilation systems from crushing and sorting equipment - elevators, crushers, transfer units, etc.;
- exhaust ventilation systems from knockout grids in foundries, land preparation equipment;
- second stage of cleaning:
- exhaust systems with high initial concentrations of contaminants - suction units from sandblasting booths and chambers.
In these scenarios, centrifugal scrubbers of class CS are widely used in exhaust ventilation systems for cleaning: they are effective in elevators, crushers and transfer units, as well as as suction units for sandblasting booths and chambers with increased initial dust concentrations.
Installation and operation features
The CS class scrubber is recommended to be installed before the fan (on the suction side) to prevent it from wear, while water is drained from the lower zone of the fan casing. The air exhaust from this unit is carried out:
- upwards, bypassing the shaft or to the side through a snail - installation of a scrubber after the fan;
- through a snail - installation of a scrubber to the fan.
In practice, it is recommended to install the CS to the fan on the suction side: this protects the impeller from wear, and water drainage is organized from the lower part of the fan casing into the drainage. Compliance with these rules increases efficiency, simplifies service and extends the life of the equipment.
For selection and purchase (CS buy, CS buy in Kiev) specify the parameters of the contaminated flow into these scrubbers, dimensions (300 ÷ 800 millimeters, 2355 ÷ 5715 millimeters) and mode (varies from 1000 to 10000 m³ / h) — Delivery and design consultation available.